主要信息
Target
ADA
Host Species
Rabbit
Reactivity
Human, Rat, Mouse,
Applications
WB, ELISA
MW
39kD (Observed)
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified
货号: YN0418
规格
价格
货期
数量
200μL
¥3,780.00
现货
0
100μL
¥2,300.00
现货
0
40μL
¥960.00
现货
0
加入购物车


已收藏


收藏
详细信息
推荐稀释比
WB 1:500-2000; ELISA 1:5000-20000
组成
Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, and 0.02% sodium azide.
特异性
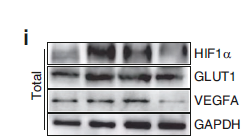
ADA Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of protein.
纯化工艺
The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
储存
-15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
浓度
1 mg/ml
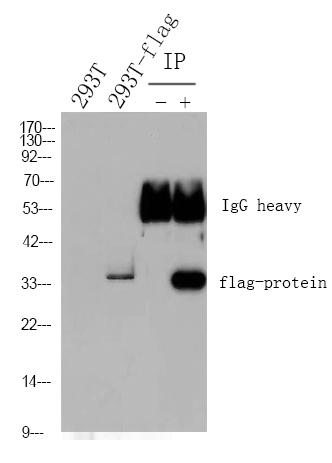
实测条带
39kD
修饰
Unmodified
克隆性
Polyclonal
同种型
IgG
相关产品
抗原&靶点信息
免疫原:
Synthesized peptide derived from human protein . at AA range: 80-160
展开内容
特异性:
ADA Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of protein.
展开内容
基因名称:
ADA ADA1
展开内容
蛋白名称:
Adenosine deaminase (Adenosine aminohydrolase)
展开内容
背景:
This gene encodes an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of adenosine to inosine. Various mutations have been described for this gene and have been linked to human diseases. Deficiency in this enzyme causes a form of severe combined immunodeficiency disease (SCID), in which there is dysfunction of both B and T lymphocytes with impaired cellular immunity and decreased production of immunoglobulins, whereas elevated levels of this enzyme have been associated with congenital hemolytic anemia. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
展开内容
功能:
Catalytic activity:Adenosine + H(2)O = inosine + NH(3).,Disease:Defects in ADA are the cause of severe combined immunodeficiency autosomal recessive T-cell-negative/B-cell-negative/NK-cell-negative due to adenosine deaminase deficiency (ADASCID) [MIM:102700]. SCID refers to a genetically and clinically heterogeneous group of rare congenital disorders characterized by impairment of both humoral and cell-mediated immunity, leukopenia, and low or absent antibody levels. Patients with SCID present in infancy with recurrent, persistent infections by opportunistic organisms. The common characteristic of all types of SCID is absence of T-cell-mediated cellular immunity due to a defect in T-cell development. ADA-SCID is an autosomal recessive form accounting for about 50% of non-X-linked SCIDs. ADA deficiency has been diagnosed in chronically ill teenagers and adults (late or adult onset). Population and newborn screening programs have also identified several healthy individuals with normal immunity who have partial ADA deficiency.,Disease:In hereditary hemolytic anemia, the level of this enzyme in erythrocytes increases 50-70 times.,online information:ADA mutation db,online information:Adenosine deaminase entry,polymorphism:There is a common allele, ADA*2, also known as the ADA 2 allozyme. It is associated with the reduced metabolism of adenosine to inosine. It specifically enhances deep sleep and slow-wave activity (SWA) during sleep.,similarity:Belongs to the adenosine and AMP deaminases family.,tissue specificity:Found in all tissues, occurs in large amounts in T-lymphocytes and, at the time of weaning, in gastrointestinal tissues.,
展开内容
细胞定位:
Cell membrane ; Peripheral membrane protein; Extracellular side. Cell junction . Cytoplasmic vesicle lumen . Cytoplasm . Lysosome . Colocalized with DPP4 at the cell surface. .
展开内容
组织表达:
Found in all tissues, occurs in large amounts in T-lymphocytes (PubMed:20959412). Expressed at the time of weaning in gastrointestinal tissues.
展开内容
研究领域:
>>Purine metabolism ;
>>Metabolic pathways ;
>>Nucleotide metabolism ;
>>Primary immunodeficiency
>>Metabolic pathways ;
>>Nucleotide metabolism ;
>>Primary immunodeficiency
展开内容
文献引用({{totalcount}})
货号: YN0418
规格
价格
货期
数量
200μL
¥3,780.00
现货
0
100μL
¥2,300.00
现货
0
40μL
¥960.00
现货
0
加入购物车


已收藏


收藏
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allToggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
主要信息
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
产品 {{index}}/{{pcount}}
上一个产品
下一个产品
{{pvTitle}}
滚轮缩放图片
{{pvDescr}}