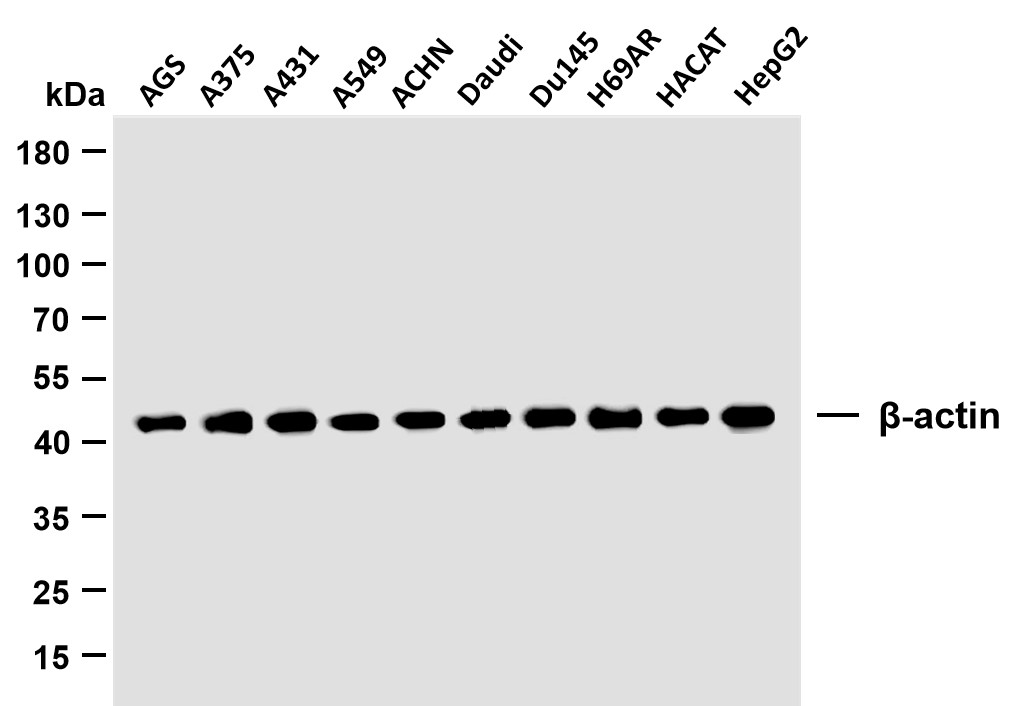
主要信息
Target
DDX58
Host Species
Rabbit
Reactivity
Human, Mouse
Applications
WB, ELISA
MW
101kD (Observed)
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified

货号: YN2110
规格
价格
货期
数量
200μL
¥3,780.00
一个月
0
100μL
¥2,300.00
一个月
0
40μL
¥960.00
一个月
0
加入购物车


已收藏


收藏
详细信息
推荐稀释比
WB 1:500-2000; ELISA 1:5000-20000
组成
Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
特异性
DDX58 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of protein.
纯化工艺
The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
储存
-15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
浓度
1 mg/ml
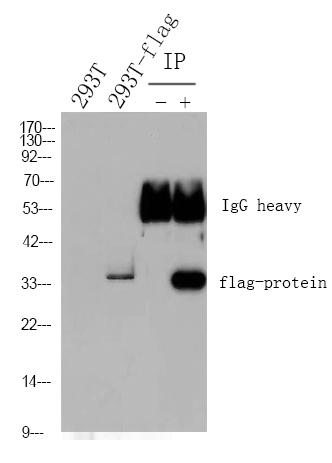
实测条带
101kD
修饰
Unmodified
克隆性
Polyclonal
同种型
IgG
相关产品
抗原&靶点信息
免疫原:
Synthesized peptide derived from part region of human protein
展开内容
特异性:
DDX58 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of protein.
展开内容
基因名称:
DDX58
展开内容
蛋白名称:
Probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX58 (DEAD box protein 58) (RIG-I-like receptor 1) (RLR-1) (Retinoic acid-inducible gene 1 protein) (RIG-1) (Retinoic acid-inducible gene I protein) (RIG-I)
展开内容
背景:
DEAD box proteins, characterized by the conserved motif Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp (DEAD), are putative RNA helicases which are implicated in a number of cellular processes involving RNA binding and alteration of RNA secondary structure. This gene encodes a protein containing RNA helicase-DEAD box protein motifs and a caspase recruitment domain (CARD). It is involved in viral double-stranded (ds) RNA recognition and the regulation of immune response. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
展开内容
功能:
Domain:The 2 CARD domains are responsible for interaction with and signaling through MAVS.,Domain:The helicase domain is responsible for dsRNA recognition.,Domain:The repressor domain controls homomultimerization and interaction with MAVS.,Function:Involved in innate immune defense against viruses. Upon interaction with intracellular dsRNA produced during viral replication, triggers a transduction cascade involving MAVS/IPS1, which results in the activation of NF-kappa-B, IRF3 and IRF7 and the induction of the expression of antiviral cytokines such as IFN-beta and RANTES (CCL5). Essential for the production of interferons in response to RNA viruses including paramyxoviruses, influenza viruses, Japanese encephalitis virus and HCV.,induction:By bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in endothelial cells. By IFN-alpha, -beta and -gamma.,PTM:Isgylated. Conjugated to ubiquitin-like protein ISG15 upon IFN-beta stimulation.,similarity:Belongs to the helicase family.,similarity:Contains 1 helicase ATP-binding domain.,similarity:Contains 1 helicase C-terminal domain.,similarity:Contains 2 CARD domains.,subunit:Monomer; maintained as a monomer in an autoinhibited state. Upon viral dsRNA binding and conformation shift, homomultimerizes and interacts with MAVS. Interacts with DHX58/LGP2, IKBKE, TBK1 and TMEM173/STING.,tissue specificity:Present in vascular smooth cells (at protein level).,
展开内容
细胞定位:
Cytoplasm. Cell projection, ruffle membrane. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Cell junction, tight junction. Colocalized with TRIM25 at cytoplasmic perinuclear bodies. Associated with the actin cytoskeleton at membrane ruffles.
展开内容
组织表达:
Present in vascular smooth cells (at protein level).
展开内容
研究领域:
>>NF-kappa B signaling pathway ;
>>RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway ;
>>Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway ;
>>Hepatitis C ;
>>Hepatitis B ;
>>Measles ;
>>Influenza A ;
>>Herpes simplex virus 1 infection ;
>>Epstein-Barr virus infection ;
>>Coronavirus disease - COVID-19
>>RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway ;
>>Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway ;
>>Hepatitis C ;
>>Hepatitis B ;
>>Measles ;
>>Influenza A ;
>>Herpes simplex virus 1 infection ;
>>Epstein-Barr virus infection ;
>>Coronavirus disease - COVID-19
展开内容
信号通路
文献引用({{totalcount}})
货号: YN2110
规格
价格
货期
数量
200μL
¥3,780.00
一个月
0
100μL
¥2,300.00
一个月
0
40μL
¥960.00
一个月
0
加入购物车


已收藏


收藏
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allToggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
主要信息
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
产品 {{index}}/{{pcount}}
上一个产品
下一个产品
{{pvTitle}}
滚轮缩放图片
{{pvDescr}}