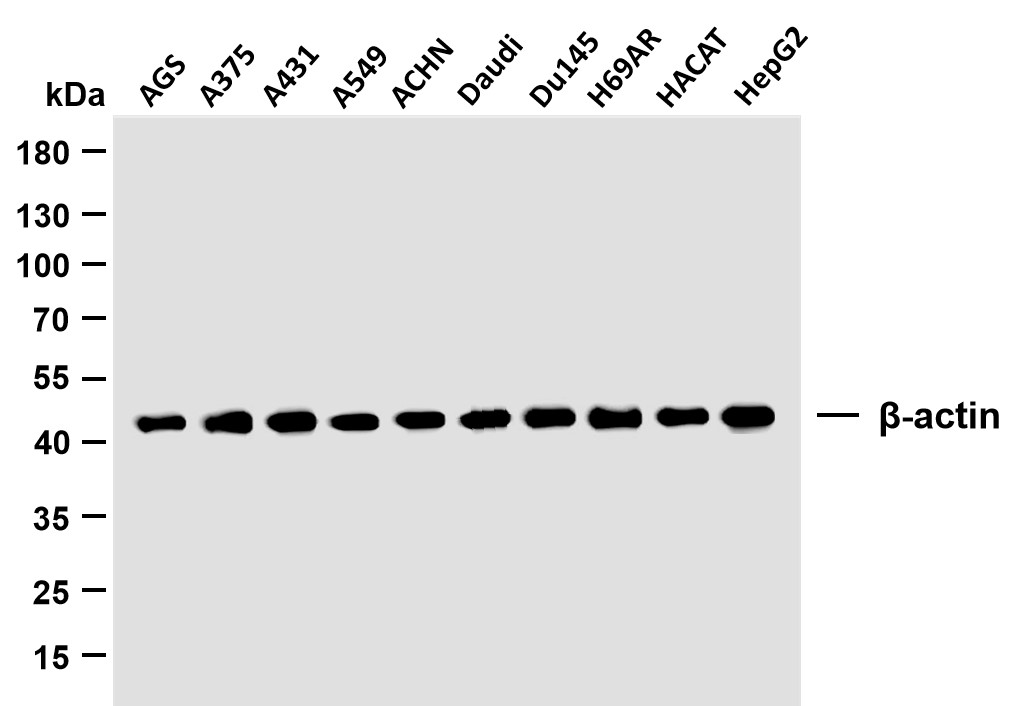
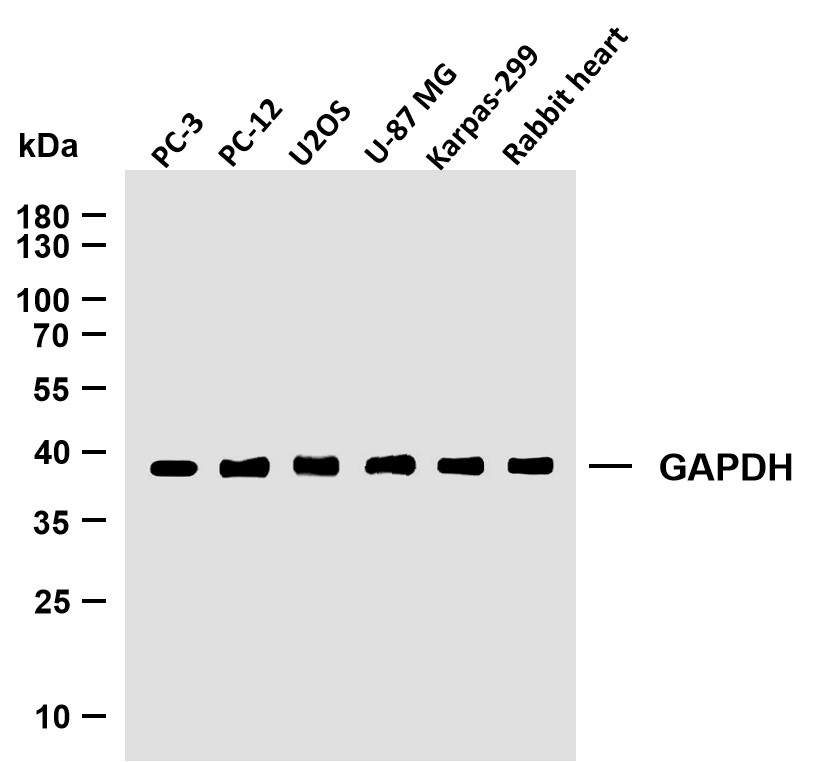
主要信息
Target
HER2
Host Species
Mouse
Reactivity
Human,
Applications
IHC
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified
货号: IHCM6883
规格
价格
货期
数量
100mL
¥14,800.00
一周
0
10mL
¥1,780.00
一周
0
3mL
¥780.00
一周
0
加入购物车


已收藏


收藏
详细信息
特异性
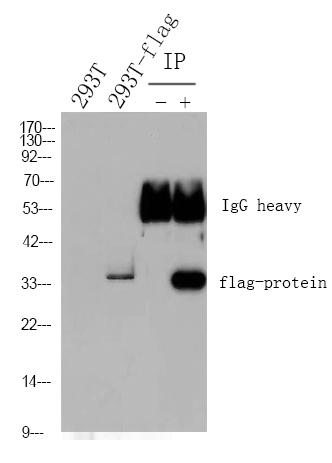
The antibody can specifically recognize human Her-2 protein.
纯化工艺
The antibody was affinity-purified from ascites by affinity-chromatography using specific immunogen.
储存
2°C to 8°C/1 year
修饰
Unmodified
克隆性
Monoclonal
克隆号
ABT077
同种型
IgG2a,Kappa
相关产品
抗原&靶点信息
免疫原:
Synthesized peptide derived from human Her-2 AA range: 300-400
展开内容
特异性:
The antibody can specifically recognize human Her-2 protein.
展开内容
基因名称:
ERBB2 HER2 MLN19 NEU NGL
展开内容
蛋白名称:
Her-2
展开内容
别名:
Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 ;
Metastatic lymph node gene 19 protein ;
MLN 19 ;
Proto-oncogene Neu ;
Proto-oncogene c-ErbB-2 ;
Tyrosine kinase-type cell surface receptor HER2 ;
p185erbB2 ;
CD antigen CD340 ;
Metastatic lymph node gene 19 protein ;
MLN 19 ;
Proto-oncogene Neu ;
Proto-oncogene c-ErbB-2 ;
Tyrosine kinase-type cell surface receptor HER2 ;
p185erbB2 ;
CD antigen CD340 ;
展开内容
背景:
This gene encodes a member of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor family of receptor tyrosine kinases. This protein has no ligand binding domain of its own and therefore cannot bind growth factors. However, it does bind tightly to other ligand-bound EGF receptor family members to form a heterodimer, stabilizing ligand binding and enhancing kinase-mediated activation of downstream signalling pathways, such as those involving mitogen-activated protein kinase and phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase. Allelic variations at amino acid positions 654 and 655 of isoform a (positions 624 and 625 of isoform b) have been reported, with the most common allele, Ile654/Ile655, shown here. Amplification and/or overexpression of this gene has been reported in numerous cancers, including breast and ovarian tumors. Alternative splicing results in several additional transcript variants, some encoding d
展开内容
功能:
Catalytic activity:ATP + a [protein]-L-tyrosine = ADP + a [protein]-L-tyrosine phosphate.,Disease:Defects in ERBB2 are associated with familial glioma of brain [MIM:137800]; also called glioblastoma multiforme. Gliomas are central nervous system neoplasms derived from glial cells and comprise astrocytomas, glioblastoma multiforme, oligodendrogliomas, and ependymomas.,Disease:Defects in ERBB2 are associated with gastric cancer [MIM:137215]; also known as hereditary familial diffuse gastric cancer (HDGC).,Disease:Defects in ERBB2 are associated with lung cancer [MIM:211980]; also called adenocarcinoma of lung.,Disease:Defects in ERBB2 are associated with ovarian cancer [MIM:167000]. Ovarian cancer is the leading cause of death from gynecologic malignancy. It is characterized by advanced presentation with loco-regional dissemination in the peritoneal cavity and the rare incidence of visceral metastases. These typical features relate to the biology of the disease, which is a principal determinant of outcome.,Function:Essential component of a neuregulin-receptor complex, although neuregulins do not interact with it alone. GP30 is a potential ligand for this receptor. Not activated by EGF, TGF-alpha and amphiregulin.,online information:ERBB2 entry,polymorphism:There are fours alleles due to the variations in positions 654 and 655. Allele B1 (Ile-654/Ile-655) has a frequency of 0.782; allele B2 (Ile-654/Val-655) has a frequency of 0.206; allele B3 (Val-654/Val-655) has a frequency of 0.012.,PTM:Ligand-binding increases phosphorylation on tyrosine residues.,similarity:Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Tyr protein kinase family. EGF receptor subfamily.,similarity:Contains 1 protein kinase domain.,subunit:Heterodimer with each of the other ERBB receptors (Potential). Interacts with PRKCABP and PLXNB1. Part of a complex with EGFR and either PIK3C2A or PIK3C2B. May interact with PIK3C2B when phosphorylated on Tyr-1196. Interacts with MEMO when phosphorylated on Tyr-1248. Interacts with MUC1. Stimulation by heregulin (HRG) in breast cancer cell lines induces binding of MUC1 with gamma-catenin.,
展开内容
细胞定位:
[Isoform 1]: Cell membrane ; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Early endosome . Cytoplasm, perinuclear region. Nucleus. Translocation to the nucleus requires endocytosis, probably endosomal sorting and is mediated by importin beta-1/KPNB1. Also detected in VPS35-positive endosome-to-TGN retrograde vesicles (PubMed:31138794). .; [Isoform 2]: Cytoplasm. Nucleus.; [Isoform 3]: Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
展开内容
组织表达:
Expressed in a variety of tumor tissues including primary breast tumors and tumors from small bowel, esophagus, kidney and mouth.
展开内容
研究领域:
>>EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance ;
>>Endocrine resistance ;
>>Platinum drug resistance ;
>>MAPK signaling pathway ;
>>ErbB signaling pathway ;
>>Calcium signaling pathway ;
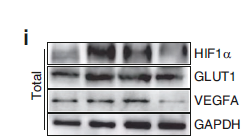
>>HIF-1 signaling pathway ;
>>PI3K-Akt signaling pathway ;
>>Focal adhesion ;
>>Adherens junction ;
>>Tight junction ;
>>Pathways in cancer ;
>>Proteoglycans in cancer ;
>>MicroRNAs in cancer ;
>>Pancreatic cancer ;
>>Endometrial cancer ;
>>Prostate cancer ;
>>Bladder cancer ;
>>Non-small cell lung cancer ;
>>Breast cancer ;
>>Gastric cancer ;
>>Central carbon metabolism in cancer
>>Endocrine resistance ;
>>Platinum drug resistance ;
>>MAPK signaling pathway ;
>>ErbB signaling pathway ;
>>Calcium signaling pathway ;
>>HIF-1 signaling pathway ;
>>PI3K-Akt signaling pathway ;
>>Focal adhesion ;
>>Adherens junction ;
>>Tight junction ;
>>Pathways in cancer ;
>>Proteoglycans in cancer ;
>>MicroRNAs in cancer ;
>>Pancreatic cancer ;
>>Endometrial cancer ;
>>Prostate cancer ;
>>Bladder cancer ;
>>Non-small cell lung cancer ;
>>Breast cancer ;
>>Gastric cancer ;
>>Central carbon metabolism in cancer
展开内容
信号通路
Cellular Processes >> Cellular community - eukaryotes >> Focal adhesion
Cellular Processes >> Cellular community - eukaryotes >> Adherens junction
Cellular Processes >> Cellular community - eukaryotes >> Tight junction
Human Diseases >> Cancer: overview >> Pathways in cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: overview >> MicroRNAs in cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: overview >> Central carbon metabolism in cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Pancreatic cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Gastric cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Bladder cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Prostate cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Endometrial cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Breast cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Non-small cell lung cancer
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> MAPK signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> ErbB signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> HIF-1 signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> Calcium signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> PI3K-Akt signaling pathway
文献引用({{totalcount}})
货号: IHCM6883
规格
价格
货期
数量
100mL
¥14,800.00
一周
0
10mL
¥1,780.00
一周
0
3mL
¥780.00
一周
0
加入购物车


已收藏


收藏
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allToggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
主要信息
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
产品 {{index}}/{{pcount}}
上一个产品
下一个产品
{{pvTitle}}
滚轮缩放图片
{{pvDescr}}