主要信息
Target
PARP
Host Species
Rabbit
Reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
Applications
WB, ELISA
MW
89kD (Observed)
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified
货号: YC0073
规格
价格
货期
数量
200μL
¥3,780.00
现货
0
100μL
¥2,300.00
现货
0
40μL
¥960.00
现货
0
加入购物车


已收藏


收藏
详细信息
推荐稀释比
WB 1:500-1:2000; ELISA 1:5000; Not yet tested in other applications.
组成
Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
特异性
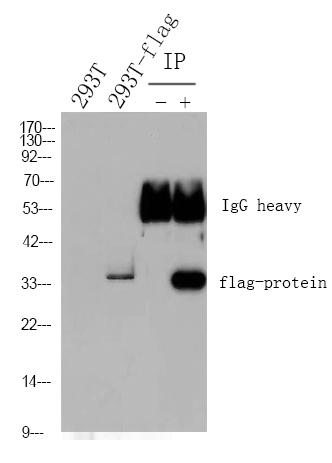
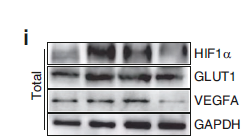
Cleaved-PARP-1 (G215) Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of fragment of activated PARP-1 protein resulting from cleavage adjacent to G215.
纯化工艺
The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
储存
-15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
浓度
1 mg/ml
实测条带
89kD
修饰
Unmodified
克隆性
Polyclonal
同种型
IgG
相关产品
抗原&靶点信息
免疫原:
The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human PARP. AA range:196-245
展开内容
特异性:
Cleaved-PARP-1 (G215) Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of fragment of activated PARP-1 protein resulting from cleavage adjacent to G215.
展开内容
基因名称:
PARP1
展开内容
蛋白名称:
Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 1
展开内容
别名:
PARP1 ;
ADPRT ;
PPOL ;
Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 1 ;
PARP-1 ;
ADP-ribosyltransferase diphtheria toxin-like 1 ;
ARTD1 ;
NAD ;
+ ;
ADP-ribosyltransferase 1 ;
ADPRT 1 ;
Poly[ADP-ribose] synthase 1
ADPRT ;
PPOL ;
Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 1 ;
PARP-1 ;
ADP-ribosyltransferase diphtheria toxin-like 1 ;
ARTD1 ;
NAD ;
+ ;
ADP-ribosyltransferase 1 ;
ADPRT 1 ;
Poly[ADP-ribose] synthase 1
展开内容
背景:
This gene encodes a chromatin-associated enzyme, poly(ADP-ribosyl)transferase, which modifies various nuclear proteins by poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation. The modification is dependent on DNA and is involved in the regulation of various important cellular processes such as differentiation, proliferation, and tumor transformation and also in the regulation of the molecular events involved in the recovery of cell from DNA damage. In addition, this enzyme may be the site of mutation in Fanconi anemia, and may participate in the pathophysiology of type I diabetes. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
展开内容
功能:
Catalytic activity:NAD(+) + (ADP-D-ribosyl)(n)-acceptor = nicotinamide + (ADP-D-ribosyl)(n+1)-acceptor.,Function:Involved in the base excision repair (BER) pathway, by catalyzing the poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation of a limited number of acceptor proteins involved in chromatin architecture and in DNA metabolism. This modification follows DNA damages and appears as an obligatory step in a detection/signaling pathway leading to the reparation of DNA strand breaks.,miscellaneous:The ADP-D-ribosyl group of NAD(+) is transferred to an acceptor carboxyl group on a histone or the enzyme itself, and further ADP-ribosyl groups are transferred to the 2'-position of the terminal adenosine moiety, building up a polymer with an average chain length of 20-30 units.,PTM:Phosphorylated by PRKDC. Phosphorylated upon DNA damage, probably by ATM or ATR.,PTM:Poly-ADP-ribosylated by PARP2.,similarity:Contains 1 BRCT domain.,similarity:Contains 1 PARP alpha-helical domain.,similarity:Contains 1 PARP catalytic domain.,similarity:Contains 2 PARP-type zinc fingers.,subunit:Component of a base excision repair (BER) complex, containing at least XRCC1, PARP2, POLB and LIG3. Homo- and heterodimer with PARP2. Interacts with PARP3, APTX and SRY. The SWAP complex consists of NPM1, NCL, PARP1 and SWAP70. Interacts with TIAM2 and ZNF423.,
展开内容
细胞定位:
Nucleus . Nucleus, nucleolus . Chromosome . Localizes to sites of DNA damage. .
展开内容
组织表达:
Brain,Colon carcinoma,Fibroblast,Lung,Ovarian carcinoma,Skin,
展开内容
研究领域:
>>Base excision repair ;
>>NF-kappa B signaling pathway ;
>>Apoptosis ;
>>Necroptosis ;
>>Diabetic cardiomyopathy
>>NF-kappa B signaling pathway ;
>>Apoptosis ;
>>Necroptosis ;
>>Diabetic cardiomyopathy
展开内容
信号通路
文献引用({{totalcount}})
货号: YC0073
规格
价格
货期
数量
200μL
¥3,780.00
现货
0
100μL
¥2,300.00
现货
0
40μL
¥960.00
现货
0
加入购物车


已收藏


收藏
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allToggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
主要信息
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
产品 {{index}}/{{pcount}}
上一个产品
下一个产品
{{pvTitle}}
滚轮缩放图片
{{pvDescr}}