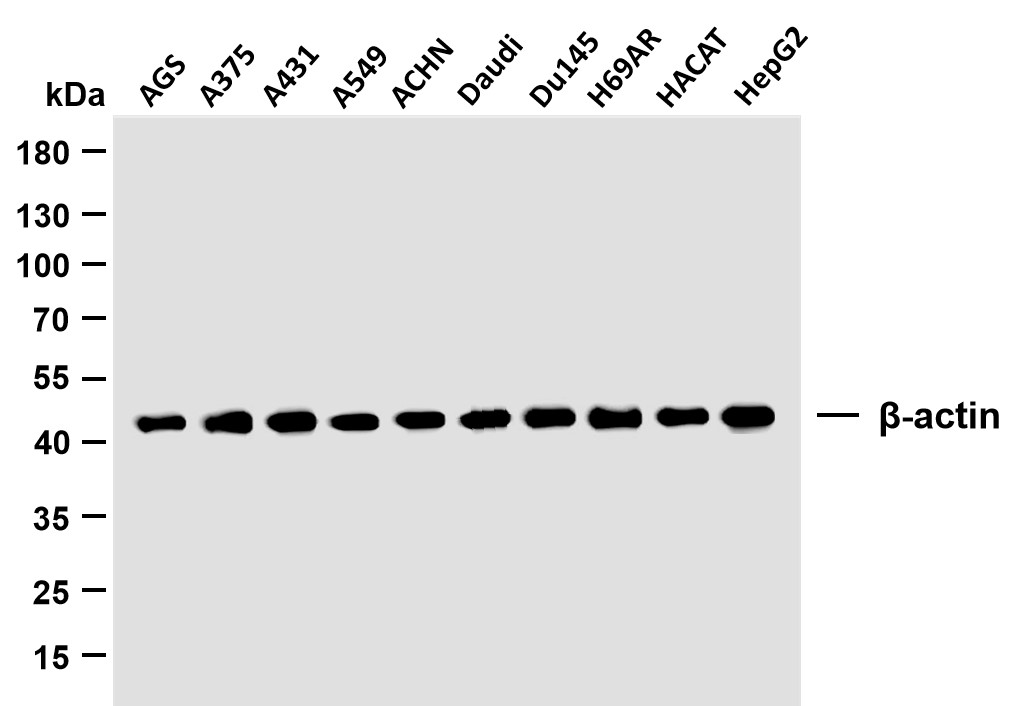
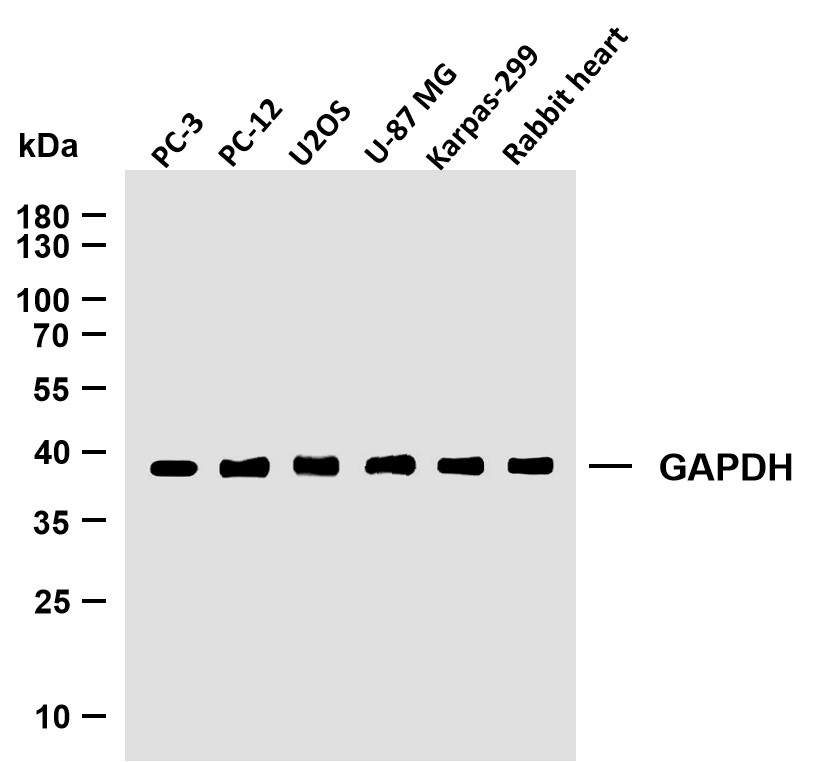
主要信息
Target
AMACR
Host Species
Mouse
Reactivity
Human,
Applications
IHC
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified
详细信息
推荐稀释比
Ready to use for IHC
组成
The prediluted ready-to-use antibody is diluted in phosphate buffer saline containing stabilizing protein and 0.05% Proclin 300
特异性
The antibody can specifically recognize human AMACR protein.
纯化工艺
The antibody was affinity-purified from ascites by affinity-chromatography using specific immunogen.
储存
2°C to 8°C/1 year
修饰
Unmodified
克隆性
Monoclonal
克隆号
ABT-AMACR
同种型
IgG1,Kappa
相关产品
抗原&靶点信息
免疫原:
Synthesized peptide derived from human AMACR AA range: 300-382
展开内容
特异性:
The antibody can specifically recognize human AMACR protein.
展开内容
基因名称:
AMACR
展开内容
蛋白名称:
AMACR
展开内容
背景:
This gene encodes a racemase. The encoded enzyme interconverts pristanoyl-CoA and C27-bile acylCoAs between their (R)- and (S)-stereoisomers. The conversion to the (S)-stereoisomers is necessary for degradation of these substrates by peroxisomal beta-oxidation. Encoded proteins from this locus localize to both mitochondria and peroxisomes. Mutations in this gene may be associated with adult-onset sensorimotor neuropathy, pigmentary retinopathy, and adrenomyeloneuropathy due to defects in bile acid synthesis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described. Read-through transcription also exists between this gene and the upstream neighboring C1QTNF3 (C1q and tumor necrosis factor related protein 3) gene. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2011],
展开内容
功能:
Catalytic activity:(2S)-2-methylacyl-CoA = (2R)-2-methylacyl-CoA.,Disease:Defects in AMACR are the cause of alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase deficiency (AMACRD) [MIM:604489]. AMACRD results in elevated plasma concentrations of pristanic acid C27-bile-acid intermediates. It can be associated with polyneuropathy, retinitis pigmentosa, epilepsy.,Disease:Defects in AMACR are the cause of congenital bile acid synthesis defect type 4 (CBAS4) [MIM:214950]; also known as cholestasis, intrahepatic, with defective conversion of trihydroxycoprostanic acid to cholic acid or trihydroxycoprostanic acid in bile. Clinical features include neonatal jaundice, intrahepatic cholestasis, bile duct deficiency and absence of cholic acid from bile.,Function:Racemization of 2-methyl-branched fatty acid CoA esters. Responsible for the conversion of pristanoyl-CoA and C27-bile acyl-CoAs to their (S)-stereoisomers.,pathway:Lipid metabolism; bile acid biosynthesis.,pathway:Lipid metabolism; fatty acid metabolism.,similarity:Belongs to the caiB/baiF CoA-transferase family.,similarity:Contains 1 C1q domain.,similarity:Contains 1 collagen-like domain.,
展开内容
细胞定位:
Cytoplasmic
展开内容
组织表达:
Aorta,Brain,Cerebellum,Kidney,Liver,PCR rescued clones,Prostate cancer,Sali
展开内容
研究领域:
>>Primary bile acid biosynthesis ;
>>Metabolic pathways ;
>>Peroxisome
>>Metabolic pathways ;
>>Peroxisome
展开内容
文献引用({{totalcount}})
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allToggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
主要信息
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
产品 {{index}}/{{pcount}}
上一个产品
下一个产品
{{pvTitle}}
滚轮缩放图片
{{pvDescr}}