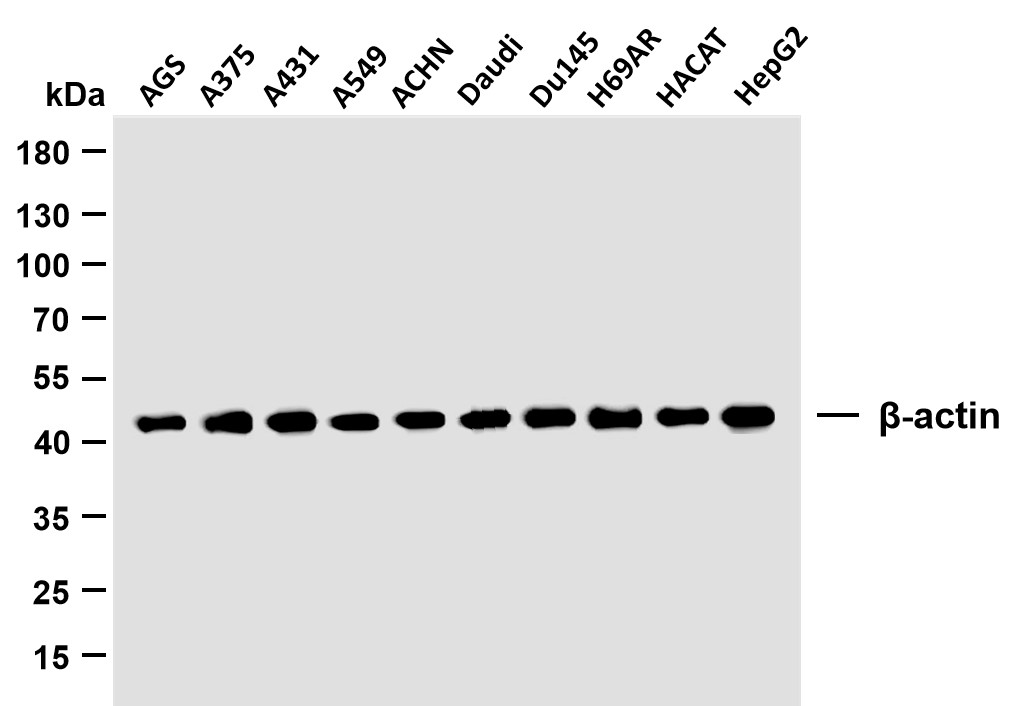
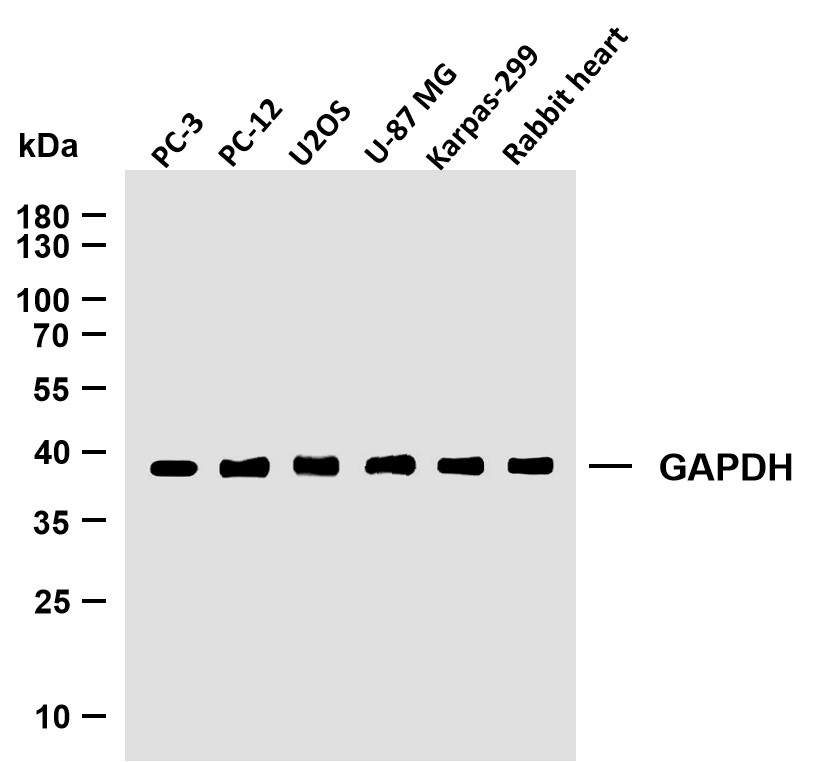
主要信息
Target
Perforin
Host Species
Rabbit
Reactivity
Human,
Applications
IHC
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified
详细信息
推荐稀释比
Ready to use for IHC
组成
The prediluted ready-to-use antibody is diluted in phosphate buffer saline containing stabilizing protein and 0.05% Proclin 300
特异性
This antibody detects endogenous levels of Perforin
纯化工艺
Recombinant Expression and Affinity purified
储存
2°C to 8°C/1 year
修饰
Unmodified
克隆性
Monoclonal
克隆号
ABT236R
同种型
IgG1,Kappa
相关产品
抗原&靶点信息
免疫原:
Synthesized peptide derived from human Perforin AA range:1-100
展开内容
特异性:
This antibody detects endogenous levels of Perforin
展开内容
基因名称:
PRF1
展开内容
蛋白名称:
Cytolysin;FLH2;HPLH2;Lymphocyte pore-forming protein;P1;PERF_HUMAN;perforin 1 (pore forming protein);Perforin 1;Perforin-1;PFP;PGFL;PIGF;PIGF-2;PLGF;Pore forming protein;prf1;SHGC-10760
展开内容
别名:
Cytolysin ;
FLH2 ;
HPLH2 ;
Lymphocyte pore-forming protein ;
P1 ;
PERF_HUMAN ;
perforin 1 ;
pore forming protein ;
Perforin 1 ;
Perforin-1 ;
PFP ;
PGFL ;
PIGF ;
PIGF-2 ;
PLGF ;
Pore forming protein ;
prf1 ;
SHGC-10760
FLH2 ;
HPLH2 ;
Lymphocyte pore-forming protein ;
P1 ;
PERF_HUMAN ;
perforin 1 ;
pore forming protein ;
Perforin 1 ;
Perforin-1 ;
PFP ;
PGFL ;
PIGF ;
PIGF-2 ;
PLGF ;
Pore forming protein ;
prf1 ;
SHGC-10760
展开内容
背景:
The protein encoded by this gene has structural and functional similarities to complement component 9 (C9). Like C9, this protein creates transmembrane tubules and is capable of lysing non-specifically a variety of target cells. This protein is one of the main cytolytic proteins of cytolytic granules, and it is known to be a key effector molecule for T-cell- and natural killer-cell-mediated cytolysis. Defects in this gene cause familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis type 2 (HPLH2), a rare and lethal autosomal recessive disorder of early childhood. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding the same protein. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
展开内容
功能:
Disease:Defects in PRF1 are the cause of familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis type 2 (FHL2) [MIM:603553]; also known as HPLH2. Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (FHL) is a genetically heterogeneous, rare autosomal recessive disorder. It is characterized by immune dysregulation with hypercytokinemia and defective natural killer cell function. The clinical features of the disease include fever, hepatosplenomegaly, cytopenia, hypertriglyceridemia, hypofibrinogenemia, and neurological abnormalities ranging from irritability and hypotonia to seizures, cranial nerve deficits, and ataxia. Hemophagocytosis is a prominent feature of the disease, and a non-malignant infiltration of macrophages and activated T lymphocytes in lymph nodes, spleen, and other organs is also found.,Function:In the presence of calcium, perforin polymerizes into transmembrane tubules and is capable of lysing non-specifically a variety of target cells.,induction:Repressed by contact with target cells.,online information:Perforin entry,online information:PRF1 mutation db,similarity:Belongs to the complement C6/C7/C8/C9 family.,similarity:Contains 1 C2 domain.,similarity:Contains 1 EGF-like domain.,similarity:Contains 1 MACPF domain.,subcellular location:Cytoplasmic granules of cytolytic T-lymphocytes.,
展开内容
细胞定位:
Cytoplasmic, Membranous
展开内容
组织表达:
Spleen
展开内容
研究领域:
>>Apoptosis ;
>>Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity ;
>>Type I diabetes mellitus ;
>>Autoimmune thyroid disease ;
>>Allograft rejection ;
>>Graft-versus-host disease ;
>>Viral myocarditis
>>Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity ;
>>Type I diabetes mellitus ;
>>Autoimmune thyroid disease ;
>>Allograft rejection ;
>>Graft-versus-host disease ;
>>Viral myocarditis
展开内容
信号通路
Cellular Processes >> Cell growth and death >> Apoptosis
Organismal Systems >> Immune system >> Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity
Human Diseases >> Immune disease >> Autoimmune thyroid disease
Human Diseases >> Immune disease >> Allograft rejection
Human Diseases >> Immune disease >> Graft-versus-host disease
文献引用({{totalcount}})
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allToggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
主要信息
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
产品 {{index}}/{{pcount}}
上一个产品
下一个产品
{{pvTitle}}
滚轮缩放图片
{{pvDescr}}